

How Does a Particle Size Analyzer Work? A particle size analyzer operates according to a specific method of measurement (for example, image analysis, laser back-scattering, or laser diffraction) with individual and method specific boundary conditions. The average particle size provides one averaged number that characterizes a larger particle population. What is the Average Particle Size? For particle populations of many different particle sizes (small to large) it is possible to calculate the arithmetic mean, median or mode as an integral function over all particles. Typical particle size measurement techniques are image analysis, laser back-scattering, laser diffraction or sieve fraction analysis. Microscopic crystals usually need more sophisticated analytical devices due to the reduced particle size. How Do You Measure Particle Size? Macroscopic particles can, for example, be measured with a ruler or caliper.
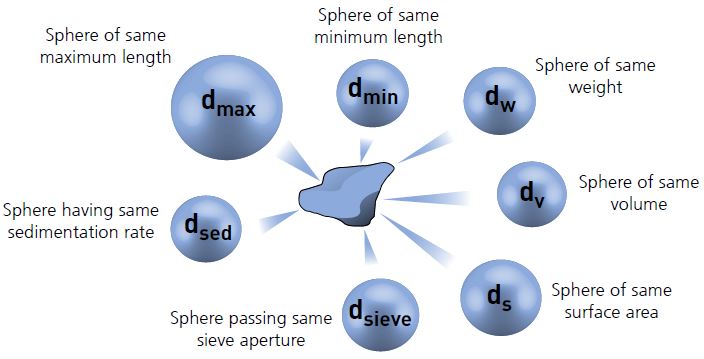
Depending on the industry and particles, a different size range can be applicable. What is Particle Size Measured In? Particle size is measured in a length dimension like nm, µm, or mm. The wrong particle size, in the worst case, can mean that a particle product will not be fit-for-purpose and a downstream process might experience an unplanned shutdown. Particle size analysis is important for process optimization and quality control to ensure and document optimal particle properties.
Particle sizer Offline#
Traditionally, sampling and offline particle size analyzers (laser diffraction, dynamic light scattering, sedimentation or sieve rest analysis) were used for product quality control. Particle size analyzers play an important role during process development and quality control of particle systems in order to develop efficient processes and achieve high final product quality. A particle size analyzer is an analytical instrument that measures, visualizes and reports a particle size distribution for a given particle or droplet population.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
